Bioinspired auditory sound localization for improving the signal to noise ratio of socially interactive robots
Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,
pages 1206--1211,
doi: 10.1109/IROS.2006.281855
- Oct 2006
In this paper we describe a bioinspired hybrid architecture for acoustic sound source localisation
and tracking to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR)
between speaker and background sources for a socially
interactive robots speech recogniser system. The model
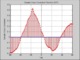
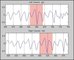
presented incorporates the use of Interaural Time Difference for azimuth estimation and Recurrent Neural Networks for trajectory prediction. The results are then presented showing the difference in the SNR of a localised and
non-localised speaker source, in addition to presenting the
recognition rates between a localised and non-localised
speaker source. From the results presented in this paper it
can be seen that by orientating towards the sound source
of interest the recognition rates of that source can be increased.
@InProceedings{MWE06,
author = {Murray, John C. and Wermter, Stefan and Erwin, Harry},
title = {Bioinspired auditory sound localization for improving the signal to noise ratio of socially interactive robots},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems},
journal = {None},
editors = {}
number = {}
volume = {}
pages = {1206--1211},
year = {2006},
month = {Oct},
publisher = {IEEE},
doi = {10.1109/IROS.2006.281855},
}