RatSLAM on Humanoids - A Bio-Inspired SLAM Model Adapted to a Humanoid Robot
Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning - ICANN 2014,
Editors: Wermter, Stefan; Weber, Cornelius; Duch, W.; Honkela, T; Koprinkova-Hristova, P.; Magg, S.; Palm, G.; Villa, A.E.P. ,
pages 789--796,
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-11179-7_99
- Sep 2014
Mapping, localization and navigation are major topics and
challenges for mobile robotics. To perform tasks and to interact efficiently
in the environment, a robot needs knowledge about its surroundings.
Many robots today are capable of performing simultaneous mapping and
localization to generate own world representations. Most assume an array of highly sophisticated artificial sensors to track landmarks placed in
the environment. Recently, there has been significant interest in research
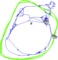
approaches inspired by nature and RatSLAM is one of them. It has been
introduced and tested on wheeled robots with good results. To examine
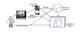
how RatSLAM behaves on humanoid robots, we adapt this model for
the first time to this platform by adjusting the given constraints. Furthermore, we introduce a multiple hypotheses mapping technique which
improves mapping robustness in open spaces with features visible from
several distant locations.


@InProceedings{MWW14,
author = {Müller, Stefan and Weber, Cornelius and Wermter, Stefan},
title = {RatSLAM on Humanoids - A Bio-Inspired SLAM Model Adapted to a Humanoid Robot},
booktitle = {Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning - ICANN 2014},
journal = {None},
editors = {Wermter, Stefan; Weber, Cornelius; Duch, W.; Honkela, T; Koprinkova-Hristova, P.; Magg, S.; Palm, G.; Villa, A.E.P.},
number = {}
volume = {}
pages = {789--796},
year = {2014},
month = {Sep},
publisher = {Springer Heidelberg},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-11179-7_99},
}