Learning Empathy-Driven Emotion Expressions using Affective Modulations
Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2018) ,
pages 1400--1407,
doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489158
- Jul 2018
Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) studies,
particularly the ones designed around social robots, use
emotions as important building blocks for interaction design.
In order to provide a natural interaction experience, these
social robots need to recognise the emotions expressed by the
users across various modalities of communication and use
them to estimate an internal affective model of the interaction.
These internal emotions act as motivation for learning to
respond to the user in different situations, using the physical
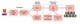
capabilities of the robot. This paper proposes a deep hybrid
neural model for multi-modal affect recognition, analysis and
behaviour modelling in social robots. The model uses growing
self-organising network models to encode intrinsic affective
states for the robot. These intrinsic states are used to train
a reinforcement learning model to learn facial expression
representations on the Neuro-Inspired Companion (NICO)
robot, enabling the robot to express empathy towards the
users.

@InProceedings{CBSW18,
author = {Churamani, Nikhil and Barros, Pablo and Strahl, Erik and Wermter, Stefan},
title = {Learning Empathy-Driven Emotion Expressions using Affective Modulations},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2018)},
journal = {None},
editors = {}
number = {}
volume = {}
pages = {1400--1407},
year = {2018},
month = {Jul},
publisher = {IEEE},
doi = {10.1109/IJCNN.2018.8489158},
}