Multiple Sound Source Localisation in Reverberant Environments Inspired by the Auditory Midbrain
This paper proposes a spiking neural network (SNN) of the
mammalian auditory midbrain to achieve binaural multiple sound source
localisation. The network is inspired by neurophysiological studies on the
organisation of binaural processing in the medial superior olive (MSO),
lateral superior olive (LSO) and the inferior colliculus (IC) to achieve
a sharp azimuthal localisation of sound sources over a wide frequency
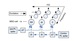
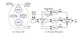
range in a reverberant environment. Three groups of artificial neurons
are constructed to represent the neurons in the MSO, LSO and IC that
are sensitive to interaural time difference (ITD), interaural level difference (ILD) and azimuth angle respectively. The ITD and ILD cues are
combined in the IC to estimate the azimuth direction of a sound source.
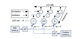
To deal with echo, we propose an inter-inhibited onset network in the IC,
which can extract the azimuth information from the direct path sound
and avoid the effects of reverberation. Experiments show that the proposed onset cell network can localise two sound sources efficiently taking
into account the room reverberation.
@InBook{LPREW09,
author = {Liu, Jindong and Perez-Gonzales, David and Rees, Adrian and Erwin, Harry and Wermter, Stefan},
title = {Multiple Sound Source Localisation in Reverberant Environments Inspired by the Auditory Midbrain},
number = {},
volume = {1},
pages = {208--2017},
year = {2009},
month = {Sep},
publisher = {Springer},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-04274-4_22},
}